We take biosecurity and health EXTREMELY seriously
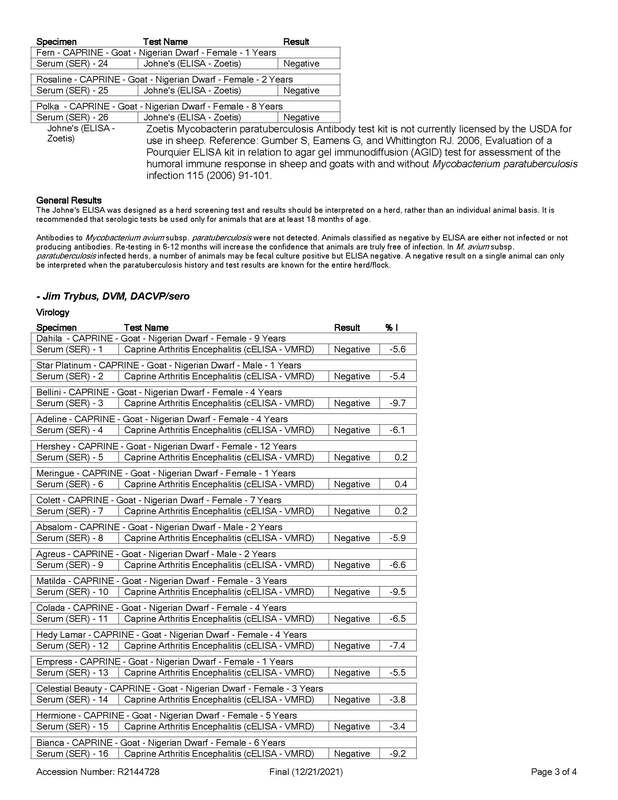
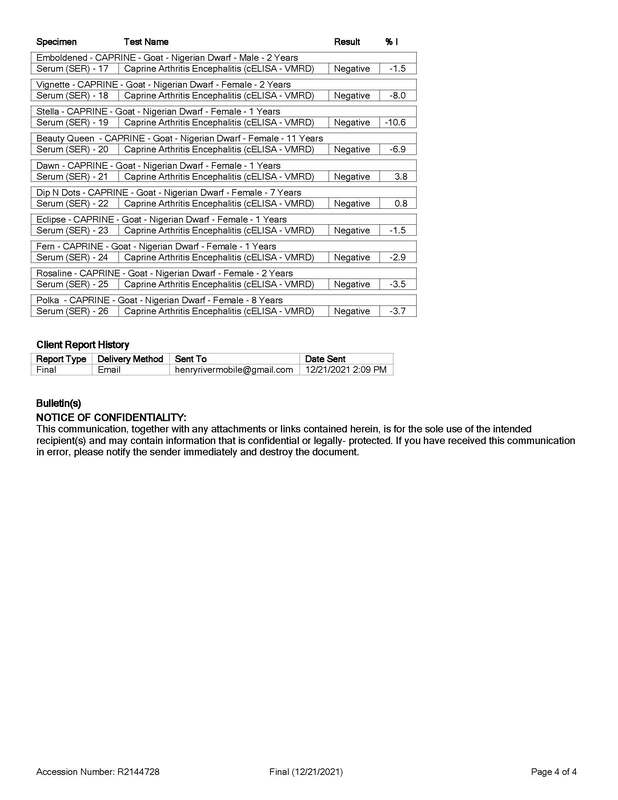
Caprine Arthritis and Encephalitis (CAE)
Caprine arthritis encephalitis (CAE) is a contagious viral disease of goats. The disease is typically spread from mother to kid through the ingestion of colostrum or milk. CAE virus may also be spread among adult goats through contact with body secretions including blood and feces of infected goats.
There are 5 major forms of CAE in goats: arthritis, encephalitis (inflammation of the brain), pneumonia, mastitis, and chronic wasting. The arthritic form of the disease is most common in adult goats, while the encephalitic form is most common in kids. The chronic wasting form of the disease can occur either seperately or in addition to any other form of CAE.
Source: articles.extension.org/pages/61393/caprine-arthritis-encephalitis-virus-cae
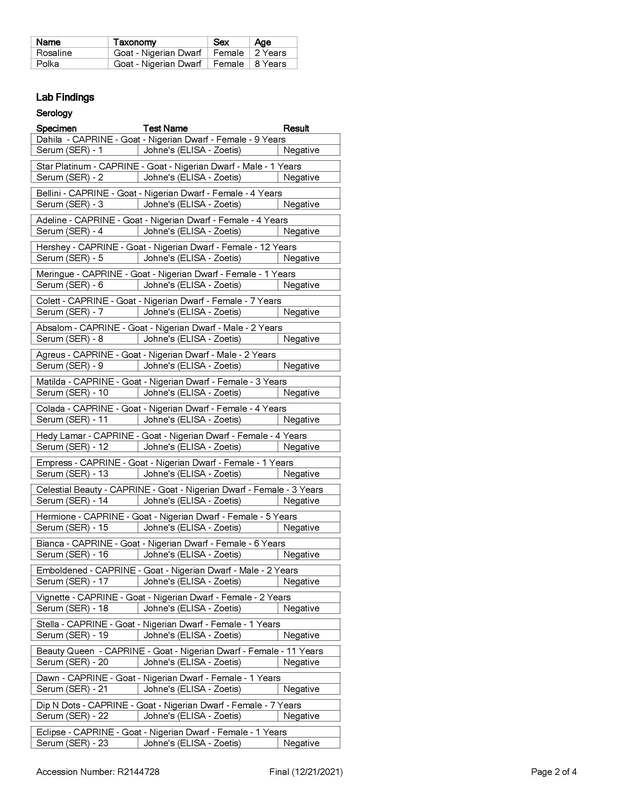
Johne's Disease
Johne’s (“YO-knees”) disease is a fatal gastrointestinal disease of goats and other ruminants (including cattle, sheep, elk, deer, and bison) that is caused by the bacterium Mycobacterium avium subspecies paratuberculosis (MAP). Also known as paratuberculosis, this infection is contagious, which means it can spread in your herd.
Source: adga.org/johnes-disease/
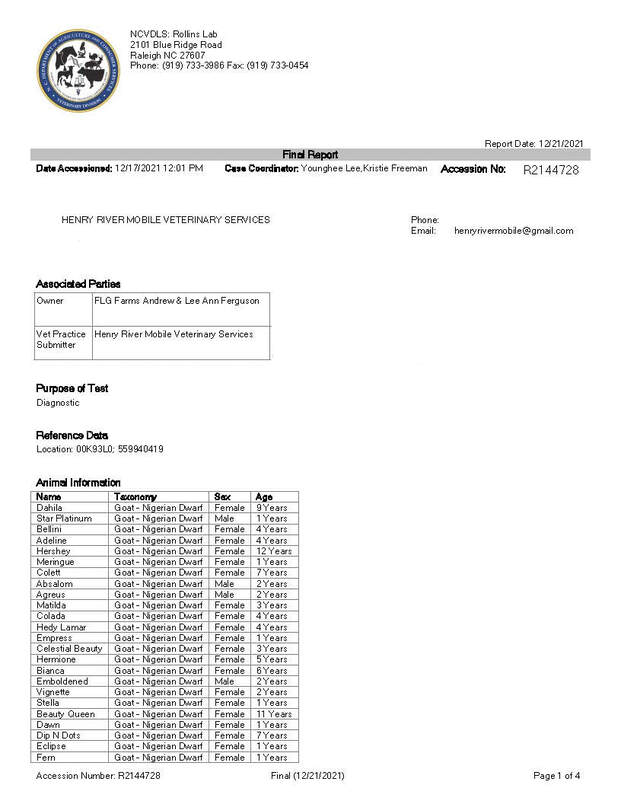
Due to the contagious nature of these diseases, we test our animals annually. Here are our most recent test results. Please note - our veterinarian recommends animals be over 6 months in age before testing. All of our animals may not be noted on all tests because of age or previous testing status.
CL: Caseous Lymphadenitis
According to the Merck Veterinarian Manual "Caseous lymphadenitis (CL) is a chronic, contagious bacterial disease that manifests clinically as abscesses of peripheral and/or internal lymph nodes and organs. The characteristic purulent material is very thick and nonodorous. Whereas the peripheral form presents as abscesses of single or multiple peripheral palpable lymph nodes, internal CL typically manifests as chronic weight loss and ill thrift. Culture of active lesions for Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis is diagnostically definitive. When eliminating animals from the herd/flock is undesirable, treatment consists of consistent, sustained antimicrobial therapy to reduce the numbers of active draining lesions and isolation from other herd mates until lesions are dry and/or resolved". To learn more, please visit https://www.merckvetmanual.com/circulatory-system/lymphadenitis-and-lymphangitis/caseous-lymphadenitis-of-sheep-and-goats
FLG Farms has had 10 years of no CL cases. Based on our trusted veterinarian recommendations, we do not blood test for CL as the test is (1) expensive and (2) is an inefficient test. Goats who have received a CL vaccination will often test positive for CL. False negative and false positive results are also very common. Because we have had no reason to suspect the presence of CL nor have we incurred any CL cysts, we claim a herd that is negative for the presence of CL.
Caprine arthritis encephalitis (CAE) is a contagious viral disease of goats. The disease is typically spread from mother to kid through the ingestion of colostrum or milk. CAE virus may also be spread among adult goats through contact with body secretions including blood and feces of infected goats.
There are 5 major forms of CAE in goats: arthritis, encephalitis (inflammation of the brain), pneumonia, mastitis, and chronic wasting. The arthritic form of the disease is most common in adult goats, while the encephalitic form is most common in kids. The chronic wasting form of the disease can occur either seperately or in addition to any other form of CAE.
Source: articles.extension.org/pages/61393/caprine-arthritis-encephalitis-virus-cae
Johne's Disease
Johne’s (“YO-knees”) disease is a fatal gastrointestinal disease of goats and other ruminants (including cattle, sheep, elk, deer, and bison) that is caused by the bacterium Mycobacterium avium subspecies paratuberculosis (MAP). Also known as paratuberculosis, this infection is contagious, which means it can spread in your herd.
Source: adga.org/johnes-disease/
Due to the contagious nature of these diseases, we test our animals annually. Here are our most recent test results. Please note - our veterinarian recommends animals be over 6 months in age before testing. All of our animals may not be noted on all tests because of age or previous testing status.
CL: Caseous Lymphadenitis
According to the Merck Veterinarian Manual "Caseous lymphadenitis (CL) is a chronic, contagious bacterial disease that manifests clinically as abscesses of peripheral and/or internal lymph nodes and organs. The characteristic purulent material is very thick and nonodorous. Whereas the peripheral form presents as abscesses of single or multiple peripheral palpable lymph nodes, internal CL typically manifests as chronic weight loss and ill thrift. Culture of active lesions for Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis is diagnostically definitive. When eliminating animals from the herd/flock is undesirable, treatment consists of consistent, sustained antimicrobial therapy to reduce the numbers of active draining lesions and isolation from other herd mates until lesions are dry and/or resolved". To learn more, please visit https://www.merckvetmanual.com/circulatory-system/lymphadenitis-and-lymphangitis/caseous-lymphadenitis-of-sheep-and-goats
FLG Farms has had 10 years of no CL cases. Based on our trusted veterinarian recommendations, we do not blood test for CL as the test is (1) expensive and (2) is an inefficient test. Goats who have received a CL vaccination will often test positive for CL. False negative and false positive results are also very common. Because we have had no reason to suspect the presence of CL nor have we incurred any CL cysts, we claim a herd that is negative for the presence of CL.